Dr James Bowen
Director Of Research
Biography
Professional biography
James joined the School of Engineering and Innovation (E&I) as Lecturer in Materials Engineering in 2015. He was promoted to Senior Lecturer in 2020 and appointed as Director of Research in 2024.
James is an expert in the application of atomic force microscopy (AFM) to topics including energy, health, pharmaceuticals, personal care, and fast-moving consumer goods. He has developed methods for performing continuous nanoscale tribological and adhesive testing across tens of square millimetres using AFM.
James’ research interests cover a wide range of topics regarding surfaces, nanomaterials, complex fluids, soft matter, and biointerfaces. James currently leads cross-disciplinary collaborative efforts within the OU STEM Faculty to develop novel processing methods for converting lunar regolith into lunar habitats and lunar infrastructure.
James works closely with colleagues whose interests include heritage and conservation, sustainability, microplastics, biomaterials, and healthcare technologies. He is progressing advanced materials characterisation techniques including high temperature X-ray diffraction as well as novel methods for the rapid determination of surface topography and roughness using non-destructive acoustic testing. His group and collaborators are investigating novel materials and surface treatments for regenerative medicine and nanomedicine, and structure-property relationships in avian eggshells.
Before joining the OU, James studied chemical engineering at the University of Birmingham. He completed his PhD researching nanoscale adhesion in 2006, studying in the School of Chemistry at the same university under the supervision of Prof. Jon Preece and Prof. Kevin Kendall FRS. He then researched the adhesive and rheological properties of liquid nanofilms, working for Prof. Mike Adams and Prof. Zhibing Zhang; the project was funded by Unilever. From 2014-2020 he was the director of Bowen Instruments Ltd, during which time he designed a range of bespoke research equipment.
James is also a passionate advocate for knowledge exchange activities. From 2009-2014 he designed and managed the ERDF-funded Science City Advanced Materials Laboratory, supporting 50 companies to successfully deliver 90 projects which addressed fundamental knowledge gaps, overcoming barriers to their growth and competitiveness. Since joining the OU, he has continued to support SMEs and charities through Knowledge Transfer Vouchers, as well as larger companies including multinationals from across the UK and EU.
PhD Projects Available
1. Lunar Habitat Construction using Lunar Regolith
2. Fracture-Resistant Anisotropic Porous Structures
3. Novel Methods for Safe Delivery of Cargo to the Lunar and Martian Surfaces
4. Nanoparticle Mechanochemistry for Carbon Dioxide Capture
5. Rheology and Processing of Liquid Metals
6. Adhesion and Tribology of Room Temperature Molten Polymers
7. Organosilicon Macromolecules for Biomedicine
Group Members
Aamina Bhutta (2025 onwards): Assessing the potential of resource extraction and utilisation of lunar and terrestrial materials through microwave processing
Jonathan Kirby (2025 onwards): Sustainable power generation using a hydroelectric siphon
Maham Hayat (2024 onwards): Reversible polymerization for the recycling of plastics and coatings
Fatemeh Khodaparastan (2023 onwards): Exploring biochar production in applied smouldering systems
Panagiotis Morfis (2023 onwards): BioPlastic Lives - developing a technical and social understanding of bioplastic objects
Ziad Mohamed (2023 onwards): Ferroelectric material for brain inspired computing
Marc Cochrane (2020 onwards): Technological pathways for international shipment of hydrogen
Christopher Spedding (2017 onwards): In-situ resource utilisation and Lunar governance
Group Alumni
Lewis Anderson (2022-2024): Synthesis of novel silsesquioxane-peptide biomaterials
Erol Hasan (2021-2022): Synthesis of novel silsesquioxane-peptide biomaterials
Donald Sale (2021-2023): Preservation and conservation of thermoplastic heritage artworks
Sunil Hettiarachchi (2018-2022): Nanoparticle and bio-lubricant additives for engine wear reduction
Yachen Jiang (2018-2019): Microwave sintering as a fabrication method for extra-terrestrial construction
Andrew Otto (2017-2024): Characterisation of good-performing graded aggregate seals
Irene Dong (2017-2023): Acoustic testing on engineering materials
Vibha Levin Prabhu (2015-2022): Microwave processing of particulate minerals
Gabriela Melo Rodriguez (2014-2017): Enhancement of titanium alloy bioactivity via peptide and hydroxyapatite coatings
Shital Lungare (2013-2016): Nasal delivery of Amantidine for the treatment of Parkinson's disease using thermoresponsive biocompatible gels
Thomas Mueller (2012-2016): Systems for measuring B cell receptor affinity maturation in germinal centres
Visiting Researchers
Hana Merchant (2023): Three-dimensional physiology of Bathyergidae specimens
Marie Caldiero (2022): Bionanoparticle synthesis and characterisation
Stephanie McClelland (2019-2020): Avian eggshell topography, structure, and function
Marie Attard (2018-2022): Evolution of avian eggshell surfaces
Nazia Mehrban (2017-2020): Surface engineering of implantable biomaterials
Shih-Chi Chu (2016-2018): Tribology of hair fibre assemblies
Jessica Andrews (2015-2016): Nanomechanical analysis of porous bioceramics
Laboratory Facilities
Our group has access to state-of-the-art equipment and facilities, including synthesis and processing, material characterisation, imaging techniques, and surface characterisation. We work with companies to solve industrially-relevant problems, and we work with conservators to help preserve objects of historical importance. We are also extablishing a facility for high-speed and high-temperature X-ray diffraction.
Research interests
James is an interdisciplinary scientist and engineer whose research involves surface modification, particle technology, polymers, rheology & complex fluids, adhesion, and the liquid/solid interface.
His interests include using nanomaterials for carbon dioxide capture, energy storage, and creating sustainable technologies. His expertise includes nanomachining, nanometrology, intermolecular & interparticle interactions, biomaterial degradation, and innovative methods of characterising complex materials. He collaborates with comparative ecophysiologists to investigate structure-property relationships in natural materials.
Research expertise
.JPG)
Teaching interests


 Powder Processing and Handling
Powder Processing and Handling
 Product Processing for Formulation (3PPF)
Product Processing for Formulation (3PPF)
Industrial Engagement
Responsible for the successful completion of 100+ projects for companies in sectors including automotive, fast-moving consumer goods, and pharmaceutical. Examples include:
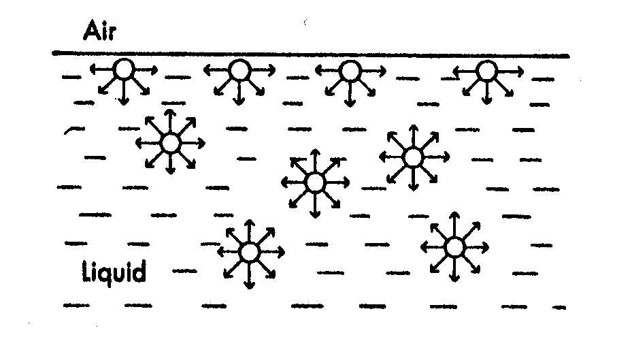
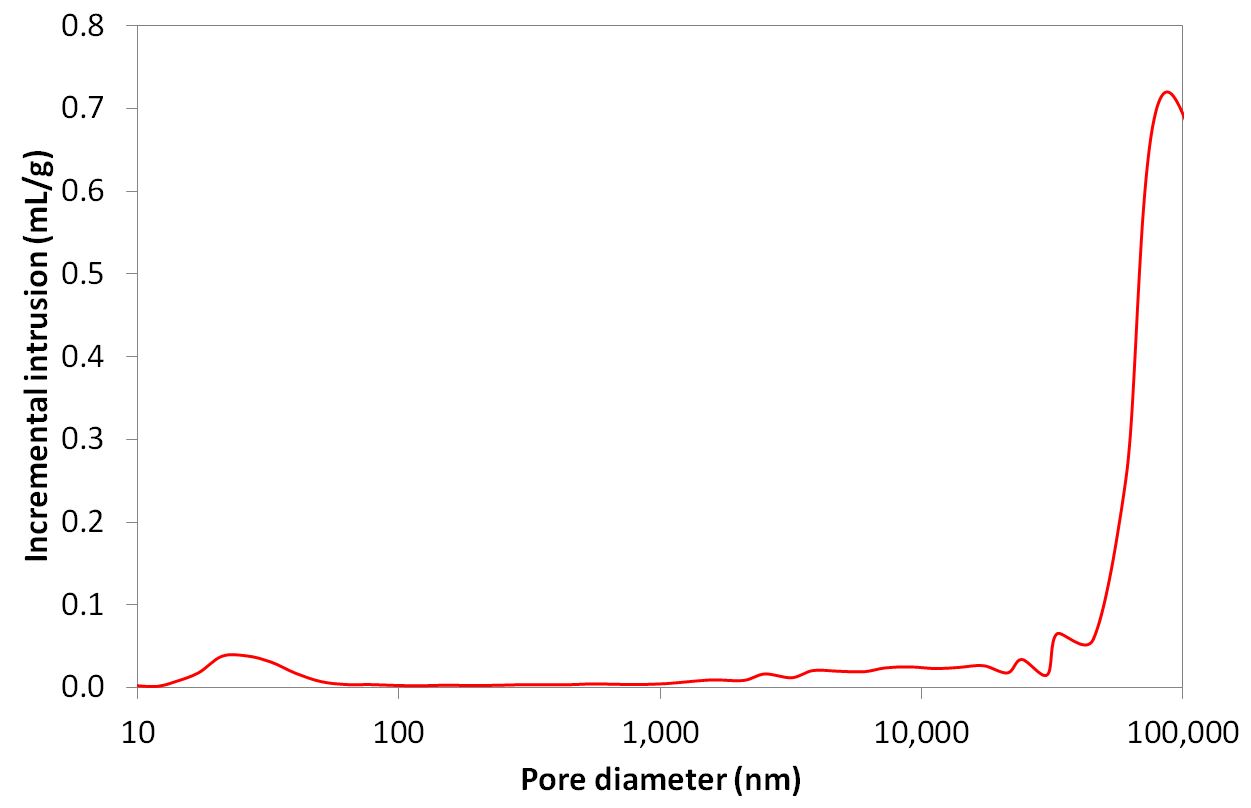 Adhesive properties and pore structure of detergent granules
Adhesive properties and pore structure of detergent granules
 Chemical and scratch resistance of printed ceramic surfaces
Chemical and scratch resistance of printed ceramic surfaces
 Design and testing of inflatable packaging
Design and testing of inflatable packaging
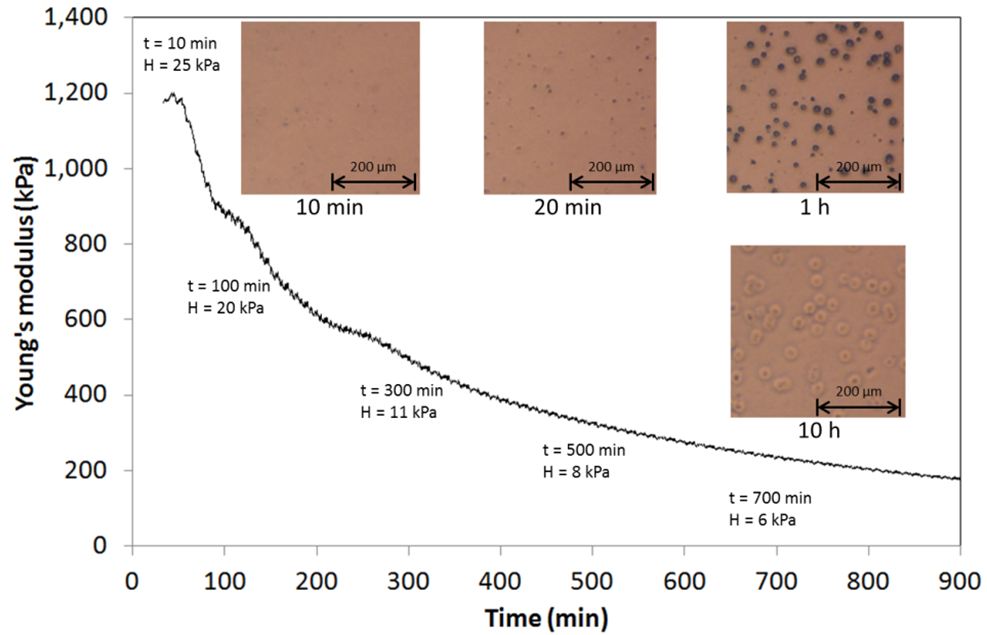 Distribution and degradation of fouling residues
Distribution and degradation of fouling residues
 Formulation of chewing gum using artificial sweeteners
Formulation of chewing gum using artificial sweeteners

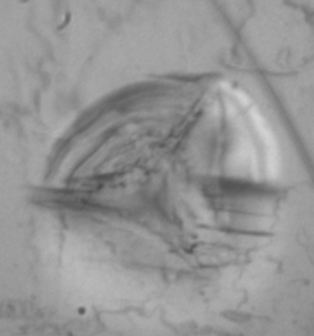 Mechanical and spectroscopic characterisation of pharmaceutical products
Mechanical and spectroscopic characterisation of pharmaceutical products
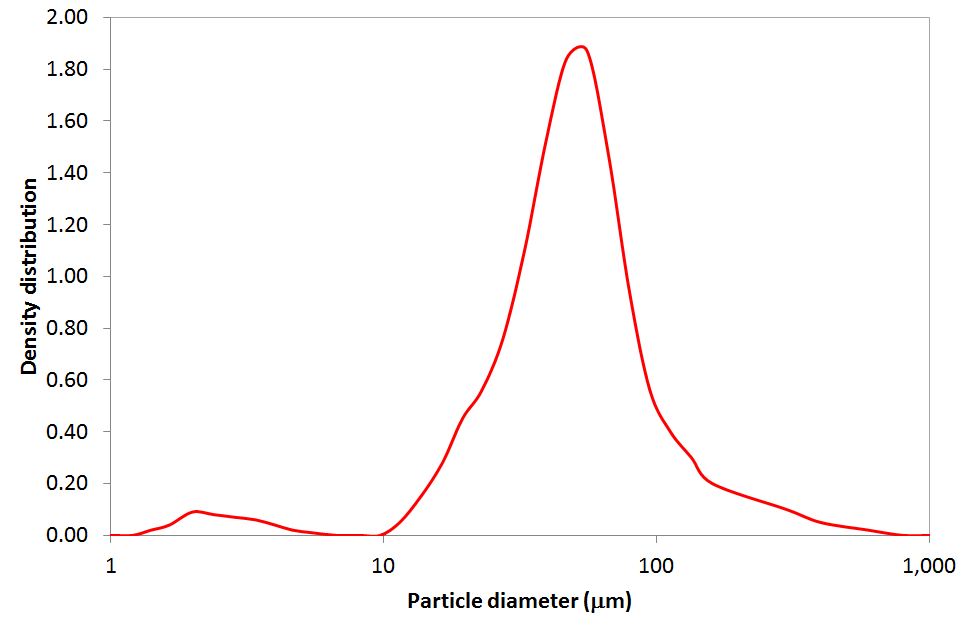 Particle size and shape distributions of powders
Particle size and shape distributions of powders
 Porosity and density of formulated products
Porosity and density of formulated products
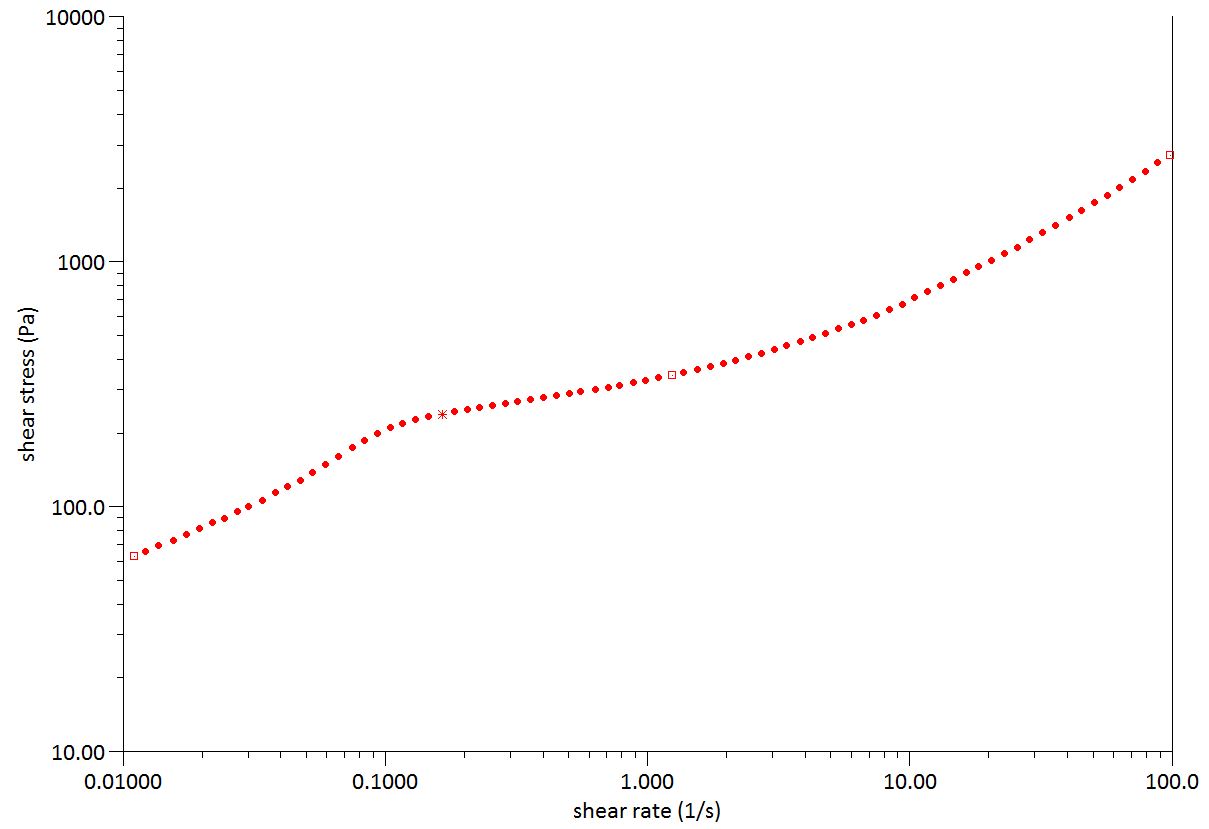 Rheological properties of epoxy resins
Rheological properties of epoxy resins
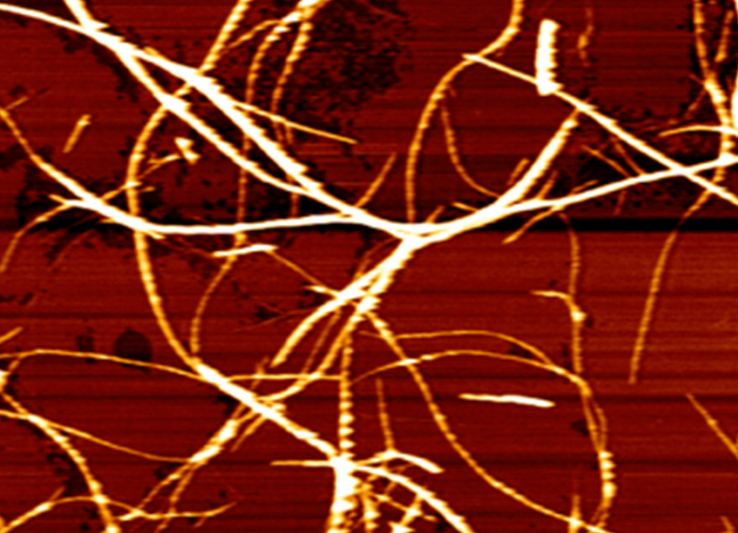 Structural characterisation of crystalline nanofibres
Structural characterisation of crystalline nanofibres
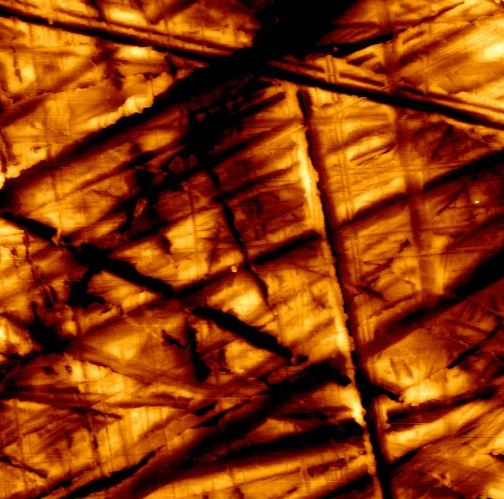 Topographical analysis of nanostructured surfaces
Topographical analysis of nanostructured surfaces
 Tribology and wear of hair fibres
Tribology and wear of hair fibres
 Water-absorbing materials for flooding attenuation
Water-absorbing materials for flooding attenuation
Projects
EM Suite (Aston Martin Aramco Formula One Team)_ XRD and SEM analysis of Ti38-644
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) images and Focused Ion Beam (FIB) cross-section and Lamella, Metallographic sample preparation, Micro-hardness testing, X-ray diffraction analysis, Raman analysis, Residual stress measurement by XRD, Hole drilling and contour method
STFC’S IMPACT ACCELERATION ACCOUNT DISCRETIONARY FUNDING 2022/23
STFC Impact Acceleration Account one year funding programme. This is a solo award made payable directly to your institution and should be used to support knowledge exchange activities for work funded through STFC’s core science programme in FY 21/22 This award includes funding for (but is not limited to): • Innovation and commercialisation proof-of concept projects • Industry / stakeholder engagement and community building workshops • Industry / stakeholder secondments This award should explicitly be used for knowledge exchange related work for the benefit of STFC-funded researchers working in one or more of the STFC core science remit areas.
Exploring Biochar Production in Applied Smouldering Systems
Given the immediate risks of climate change, bold carbon sequestration initiatives are needed. Biochar production has been suggested as one such initiative. Biochar is a carbon-rich by-product of thermal processing biomass, typically via pyrolysis, and its application in agricultural systems has been demonstrated as a viable method to improve soil quality. However, pyrolysis units rely on endothermic reactions and therefore require external energy, which can lead to process complexity. Applied smouldering is emerging as valuable environmental engineering technology due to its robustness and simplicity. Applied smouldering systems have been demonstrated suitable for a range of applications: e.g., for waste-to-energy, remediation, resource recovery/generation, and off-grid sanitation in low-income countries. Smouldering is a flameless, low-temperature form of combustion that is harnessed in these systems to support a self-sustaining process without the need for external energy. These systems are highly energy efficient and can therefore manage problematic wastes, e.g., with high moisture content or low volatility. Given the simplicity of applied smouldering systems, they have the potential to be deployed worldwide to produce biochar from biomass wastes for carbon sequestration and soil improvement. Indeed, recent research has demonstrated this potential. However, the processes that lead to biochar production are not yet well-understood. Smouldering systems are dynamic in space and time and support numerous physical and chemical zones. Generally, pyrolysis reactions proceed ahead of combustion reactions, but they also overlap and compete in space. Therefore, improved understanding of how these reactions establish in applied smouldering systems through experimental methods will provide guidance on how to best maximise biochar production in a self-sustaining manner. Moreover, the energy balance and carbon sequestration results from these systems will need to be quantified to model the potential scale-up benefits. Last, it is not clear how beneficial the biochar from smouldering systems is compared to biochar generated from traditional pyrolysis methods. These are key research questions that limit the development of applied smouldering systems for carbon sequestration. Methodology: This research will use established smouldering experimental methods to produce biochar. These experiments will investigate strategies to maximise biochar output and quantify the carbon and energy balances, following established methods. In addition, biochar formation in controlled pyrolysis units will be completed in-house to provide comparative samples. Biochar samples produced from smouldering and pyrolysis systems will be compared via surface science analyses.
Analysing the Reuse of Single-use Plastics in the Chemical Laboratory
Within the chemical laboratory, plastic items are widely used as they provide cheap and convenient options but in recent years the environmental cost of using single-use plastics in labs has been highlighted and so we aim to analyse their reuse. Although plastic items are renowned for their durability, it is known that exposure to UV, abrasion and chemical agents can damage the surface of plastics. Consequently, there is a need to evaluate how single-use plastics may be cleaned and recycled in the laboratory in connection with any deterioration in their properties with each use-cleaning cycle
Microwave heating Apparatus of lunar Regolith for Variant Experiments of Lunar ISRU missions
For an extended stay on the Moon, humans require habitation with substantial protection from space radiation and micrometeorites. The lunar regolith is a readily available resource in-situ, which could be thermally treated to extract oxygen and water as well as build lunar surface elements, e.g., lunar habitats, landing pad and path using 3D printing techniques. Due to the volumetric heating characteristic intrinsic to microwave heating, it is a much more efficient process than solar or laser sintering for large-scale manufacturing and construction. Our proof of concept experiment has demonstrated that microwave energy couples efficiently with lunar simulants and can readily heat it above the melting temperature. However, testing with lunar simulants cannot fulfil some missing information on microwave heating of lunar regolith, which includes the effects of nanophase iron and highly electrostatic and irregular particle shapes under the real lunar environment, i.e. vacuum and microgravity. Therefore, we aim to develop flight hardware of MARVEL (Microwave heating Apparatus of lunar Regolith for Variant Experiments of Lunar ISRU) as a payload for future ESA lunar ISRU missions. MARVEL will (i) collect and compact three samples (25~50g); (ii) heat the samples with 250 W of input power for 60 minutes; and (iii) measure the temperature and volatile release profile every second until it is cooled down to ambient temperature; to demonstrate the potential of microwave heating for construction and oxygen/water extraction. The ESA’s ISRU demonstrator mission includes a core payload to demonstrate oxygen extraction from lunar soils and secondary payloads demonstrating other aspects of lunar ISRU. Our proposed MARVEL payload could potentially address both these challenges with a unique and enabling technology for Europe. The initial concept of MARVEL at TRL 2, submitted to the ESA RFI of Lunar ISRU Demonstration Platform in December 2018, has made more progress with new consortium members. With the success of this project, we will (i) develop a model of microwave heating behaviour of lunar regolith under lunar conditions; and (ii) establish crucial criteria for developing a microwave heating-based fabrication method, including 3D Printing.
Nanoscale surface topography of electron beam hardmask thin films
Two regions of a 300 mm wafer will be analysed: Centre Edge The wafer is coated with a carbon-based hardmask thin film, to be used as an electron beam resist, for nanolithography. AFM images will be recorded at each location. Surface topography images will be presented. Surface roughness will be analysed. Two wafers will be measured.
Silicon microcantilevers for tribological tests
Andrew Avery at Unilever R&D Port Sunlight, with whom I have a long-standing collaborative relationship, has asked me to manufacture a batch of silicon microcantilevers. I will keep these for our future projects together. These cantilevers have been used in the Projects: 1560201: Single Fibre Tribometer Throughput Study 590478: Feasibility Study for a new Fibre Friction Measurement Methodology Specification: Thickness = 12.5 um Width = 50 um Length = 550 um Spring Constant = 22.3 N/m Resonant Frequency = 54.7 kHz These cantilevers worked really well during our previous projects. They are mechanically stable and resistant to twisting during sliding. A cantilever with typical thickness (0.5-2.0 um) would not be as resistant to twisting. They are manufactured bespoke by Nu Nano Ltd, one silicon wafer at a time, yielding around 250-300 cantilevers: Cantilever reference: 10A Quotation: NNQ20060 Cost ex. VAT: GBP 6,373.00
National Facility for High Speed and High Temperature X-Ray Diffraction
This facility will be a capability unique in Europe, providing pioneering materials characterisation measurements for engineers, chemists, physicists, and materials scientists. It will enable transformative research programmes under the EPSRC themes of Energy, Engineering, Global Uncertainties, Healthcare Technologies, Manufacturing the Future, Physical Sciences, Quantum Technologies, and Research Infrastructure, achieved through the provision of a remotely accessible facility capable of measuring structural changes in materials during temperature ramps.
Self-Assembled Polar and Non-Polar Surfaces
Manufacture of polar and non-polar surfaces for Omya, Switzerland Polar = OH surface Non-polar = CH3 surface 5 units for each surface type Project requires JB to spend 3-4h in a lab with a fume cupboard The surfaces will be manufactured using surface active self-assembly of commercially available molecules Project to be performed as soon as JB can access Venables laboratories
Cavity development for the Microwave Heating Demonstrator (MHD) payload concept
Humans are explorers, and the Moon is expected to play a vital role in our endeavour to expand our presence into space. However, a sustainable and affordable exploration of the Solar System cannot rely solely on Earth’s resources and must use materials obtained and processed locally. The current road map agreed upon by several international space agencies envisages a long-duration presence on the Moon by 2028, initiated through the Lunar Orbital Platform Gateway and supported by commercial service providers. A key aim of this road map is to enable development of In-Situ Resource Utilisation (ISRU) to minimise dependency on transporting all resources from Earth. ISRU is a rapidly growing field in Europe as evidenced by recent ISRU workshop in 2019, organised by ESA with over 350 participants from academia and industry. Water, required for life support and propellant, has been identified as the primary resource. However, for an extended stay on the Moon, humans will require habitats with substantial shielding from radiation and micrometeorites damage. Thus, ESA is planning ISRU demonstrator missions by mid to late 2020s, with a core payload provided by industry to demonstrate oxygen extraction from lunar regolith (soil) as well as secondary payloads for demonstrating other aspects of lunar ISRU. For example, lunar regolith could be thermally treated to extract resources and build an outer habitat shell using additive manufacturing techniques (a.k.a. 3D printing) by robots. Proof of concept experiments have demonstrated that microwaves couple efficiently with lunar regolith and sinter/melt it to build 3D structures and enable resource extraction. The Open University (OU) has an extensive ongoing programme of lunar research, including a rich heritage in spacecraft instrumentation, e.g., Ptolemy and the ProsSPA instruments, of which the latter will perform first ISRU demonstration of producing water on the Moon through reduction of regolith using hydrogen. The OU has also recently invested in a custom-designed microwave instrument to evaluate the heating of planetary materials under vacuum; progressing microwave heating experiments from traditional microwaves in the air to a controllable microwave heating in a simulated space environment. Added Value Solutions UK Ltd. (AVS) designs bespoke solutions for space science markets and are developing thrusters using microwave generators designed by VIPER RF, a microwave design consultancy. Thus, the OU has initiated a collaborative project MARVEL (Microwave heating Apparatus for Regolith Variant Experiments for Lunar ISRU) with AVS and VIPER to prepare the groundwork for the UK to lead development of a Microwave Heating Demonstrator (MHD) payload on future missions to the Moon with the flight hardware being developed and built in the UK. The initial concept development of the MHD payload was successfully completed with support from UKSA’s NSTP GEI funding. As a follow-up of the GEI project, this NSTP Pathfinder grant will allow the consortium to develop a complete (including design) concept of the MHD payload. The main objectives of this project are to: (i) develop the detailed features and functional integration of the microwave cavity design, (ii) evaluate the cavity design through computational simulation, and lab-based experiment using the existing bespoke microwave heating system with specific parameters for the MHD payload, (iii) devise a realistic concept and analyse the requirement for developing 1 kW solid-state microwave generator, which can be included in the MHD payload, and (iv) develop a robust payload concept of MHD, and exploit the technological advancements arising from this project to place the UK industry at the forefront of lunar ISRU missions such as ESA’s ISRU demonstrator mission and NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program. The successful completion of the proposed project will increase the TRL of the MHD payload from 2 to 3/4.
Nanoindentation of Bovine Teeth - (BU0065/15)
StressMap has been requested to conduct nanoindentation measurements on bovine teeth.
TOPOGRAPHY AND SURFACE OF AU THIN FILMS - (BU0066/15)
StressMap has been requested to conduct topography and surface of Au thin films.
Temperature-dependent physical properties of microcapsules (BU0092-16)
StressMap has been requested to conduct an assessment of the temperature-dependent physical properties of polymer microcapsules. Three samples are to be analysed using Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM).
Publications
Book Chapter
Monitoring biomineralization of biomaterials in vivo (2016)
The influence of wetting on the buoyancy of particles (2011)
Journal Article
The viscosity and processing of molten lunar regolith (2025)
Scratching beyond the surface: examining macroecological patterns in avian eggshell texture (2025)
Oxygen dynamics in smouldering combustion: Impacts on reaction zones and biochar production (2025)
Enhancing physicochemical properties of coconut oil for the application of engine lubrication (2023)
Surface texture heterogeneity in maculated bird eggshells (2023)
Ecological drivers of eggshell wettability in birds (2021)
α-Helical Peptides on Plasma-Treated Polymers Promote Ciliation of Airway Epithelial Cells (2021)
Polydopamine Linking Substrate for AMPs: Characterisation and Stability on Ti6Al4V (2020)
Selective modification of Ti6Al4V surfaces for biomedical applications (2020)
Host macrophage response to injectable hydrogels derived from ECM and α-helical peptides (2020)
Precise generation of selective surface-confined glycoprotein recognition sites (2019)
Improving cellular migration in tissue-engineered laryngeal scaffolds (2019)
The stability and degradation of PECVD fluoropolymer nanofilms (2019)
Silsesquioxane polymer as a potential scaffold for laryngeal reconstruction (2018)
On the electrical conductivity of alginate hydrogels (2018)
Plasma Jet Printing and in Situ Reduction of Highly Acidic Graphene Oxide (2018)
Mechanical characterization of torsional micro-paddles using atomic force microscopy (2018)
Selecting suitable image dimensions for scanning probe microscopy (2017)
Liquid-like behaviour of gold nanowire bridges (2017)
Facile synthesis of novel hybrid POSS biomolecules via “Click” reactions (2017)
Development of MIL-101(Cr)/GrO Composites for adsorption heat pump applications (2017)
Confirmation of a Nanohybrid Shish-Kebab (NHSK) Structure in Composites of PET and MWCNTs (2017)
Anisotropic dehydration of hydrogel surfaces (2017)
Friction and wear of human hair fibres (2016)
Adhesion between silica surfaces due to hydrogen bonding (2016)
Adhesion of Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms to glass, stainless steel and cellulose (2016)
Development and Evaluation of a Novel Intranasal Spray for the Delivery of Amantadine (2016)
On the origin and magnitude of surface stresses due to metal nanofilms (2016)
Effects of current on early stages of focused ion beam nano-machining (2015)
Nanoscale crystallinity modulates cell proliferation on plasma sprayed surfaces (2015)
Graphene-based ultrathin flat lenses (2015)
Mechanical properties of alginate hydrogels manufactured using external gelation (2014)
The effects of dwell time on focused ion beam machining of silicon (2014)
Adhesion of perfume-filled microcapsules to model fabric surfaces (2014)
Nitrogen plasma surface modification enhances cellular compatibility of aluminosilicate glass (2013)
Structural changes to resorbable calcium phosphate bioceramic aged in vitro (2013)
Spherical indentation analysis of stress relaxation for thin film viscoelastic materials (2013)
Optimised determination of viscoelastic properties using compliant measurement systems (2013)
Active screen plasma nitriding enhances cell attachment to polymer surfaces (2013)
A novel water-based cathode ink formulation (2013)
Controlling thin liquid film viscosity via modification of substrate surface chemistry (2013)
Degradation of polymer films (2013)
Investigation of techniques for the measurement of articular cartilage surface roughness (2013)
Dielectric properties of pulsed-laser deposited indium tin oxide thin films (2012)
Rapid manufacture of monolithic micro-actuated forceps inspired by echinoderm pedicellariae (2012)
A dynamic model of the jump-to phenomenon during AFM analysis (2012)
Direct e-beam lithography of PDMS (2012)
Prediction of inter-particle adhesion force from surface energy and surface roughness (2012)
Adhesion of alumina surfaces through confined water layers containing various molecules (2012)
Residual stress analysis of all perovskite oxide cantilevers (2011)
Fabrication and analysis of cylindrical resin AFM microcantilevers (2011)
Engineering biofilms for biocatalysis (2011)
Characteristics and durability of fluoropolymer thin films (2011)
Nanodots induced columnar growth of YBa2Cu3Ox films (2010)
Effect of plasma surface modification on the biocompatibility of UHMWPE (2010)
Pinning potential in thick PrBa2Cu3Ox/YBa2Cu3O7−δ quasi-multilayers (2009)
Microstructure–property relationships in thin film ITO (2009)
The adhesive properties of pyridine-terminated self-assembled monolayers (2009)
The pH-dependent adhesion of nanoparticles to self-assembled monolayers on gold (2008)
AFM characterisation of silicon-on-insulator push-in plates for Casimir force measurements (2008)
Presentation / Conference
Nanoscale tribology of hair fibres over large displacements (2024)
Solvent-induced softening of polymethyl methacrylate surfaces (2024)
Manufacture and calibration of high stiffness AFM cantilevers (2024)
Plug and play nanoparticles: functionalization of octa-alkyne silsesquioxane nanocages (2021)
Nanoscale tribology over large displacements (2021)
Rapid assessment of surface topography via non-destructive acoustic testing (2021)
Nanotechnology in 21st Century Healthcare Research (2021)
Manufacture and calibration of high stiffness AFM cantilevers (2021)
Manufacture and calibration of high stiffness AFM cantilevers (2020)
Assessing engineered materials via non-destructive impact acoustics (2019)
Spin-on-carbon hard masks utilising fullerene derivatives (2016)
Predicting the behaviour of micro/nanoparticles in lung lining fluid (2015)
The adhesive properties of viscoelastic liquid films (2015)
Electrospray synthesis of PLGA TIPS microspheres (2015)
Functionalization of biomedical surfaces by peptide aptamers (2015)
Fullerene derivative based spin-on-carbon hard masks for advanced lithographic applications (2015)
Nano-hydroxyapatite deposition on titanium using peptide aptamers (2015)
Electrospray synthesis of PLGA TIPS microspheres (2015)
High temperature reliability of power module substrates (2015)
Failure behaviour of AZO/Ag/AZO multilayers on PEN substrates for flexible electronic devices (2015)
Functionalization of biomedical surfaces by peptide aptamers (2015)
Fabrication of double ended tuning fork using ALD Al2O3 as a hard mask (2014)
Pixel spacing effects for nanofabrication using focused ion beam (2014)
Elucidating the biological role of soluble silicon in early bone mineralisation (2014)
Systems for measuring B cell receptor affinity maturation in germinal centres (2014)
Adhesion attenuation and enhancement in aqueous solutions (2014)
Measuring viscoelastic properties using compliant systems (2014)
Effects of focused ion beam dwell time on nano fabrication (2013)
Angular effects in focused ion beam milling of silicon (2013)
Monitoring mineralisation in hydrogels at the engineered hard/soft tissue interface (2013)
NEMS based tactile sensing in an artificial finger (2013)
Towards rapid manufacture of externally gelated tissue analogues (2013)
Characterization of microcapsule adhesion on cellulose film by a flow chamber and AFM (2013)
Overcoming Parkinson’s disease: direct nose-to-brain delivery of amantadine (2013)
The effect of aperture size on gigaseal formation (2013)
Optimisation of nanoscale surface topography analysis (2012)
In vitro formation and maturation of a hard/soft tissue interface (2012)
Surface functionalisation of silicon-substituted apatite xerogels (2012)
Direct e-beam lithography of PDMS (2011)
Friction of hair fibres: effects of load, speed and sliding direction (2011)
The influence of wetting on the buoyancy of particles (2011)
The measurement and analysis of the adhesion arising from non-Newtonian liquid bridges (2011)
New multilayer architectures for piezoelectric BaTiO3 cantilever systems (2011)
In vitro ageing of 3D printed brushite cement in culture media (2010)
Effect of active screen plasma nitriding on the biocompatibility of UHMWPE surfaces (2010)
Surface modification of silicon substituted apatite (2009)
On the capillary/viscous force transition in pendular liquid bridges (2009)
FIB direct write of ALD Al2O3 mask for silicon DRIE (2008)
Fabrication of a metamaterial to modify the Casimir force (2008)
Life in the slip lane: the effect of molecular level friction on algal adhesion (2006)
A model for nanoparticle gene delivery systems (2003)
Accurate micron-scale modification of AFM cantilevers (2002)
Presentation / Conference Contribution
MXene-based Memristive Devices for Enhanced Synaptic Functionality (2025)
 Atomic Force Microscopy
Atomic Force Microscopy Confocal Raman Microscopy
Confocal Raman Microscopy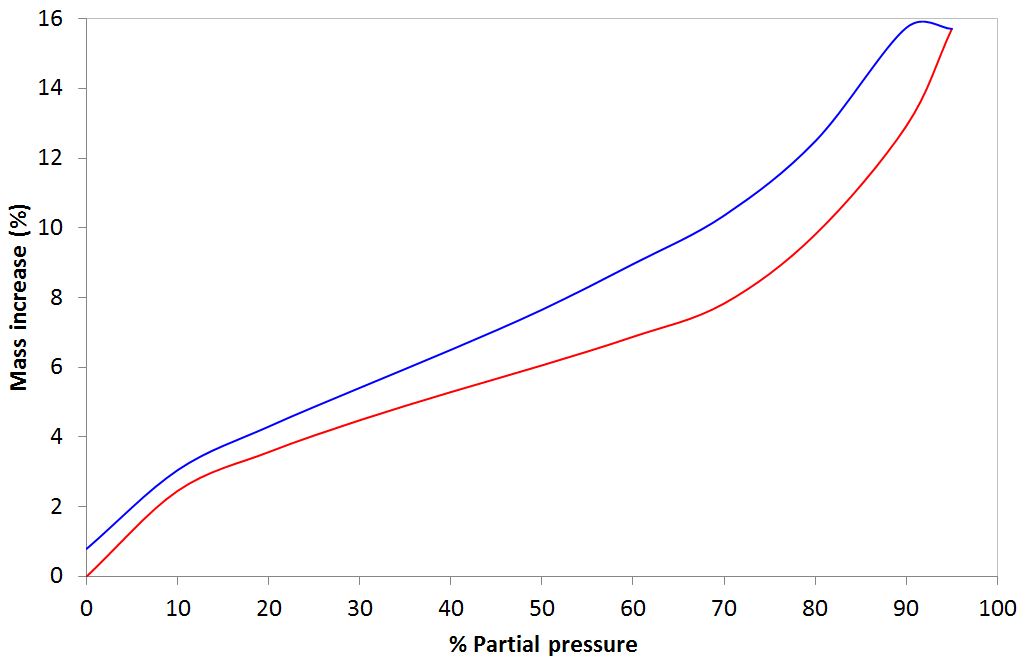 Dynamic Vapour Sorption
Dynamic Vapour Sorption.JPG) Electron Microscopy
Electron Microscopy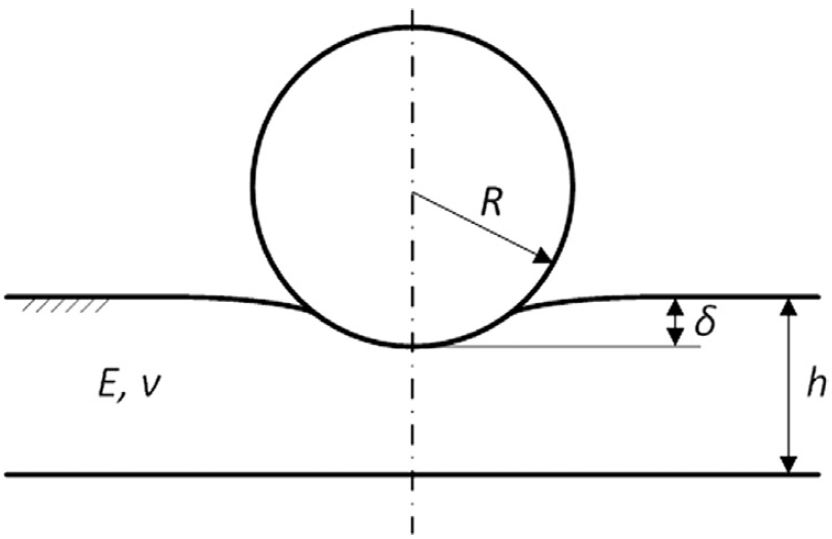 Mechanical Testing
Mechanical Testing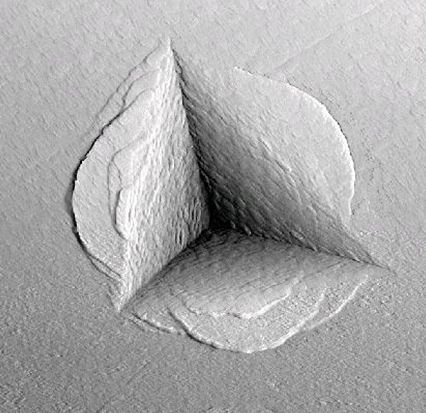 Nanoindentation
Nanoindentation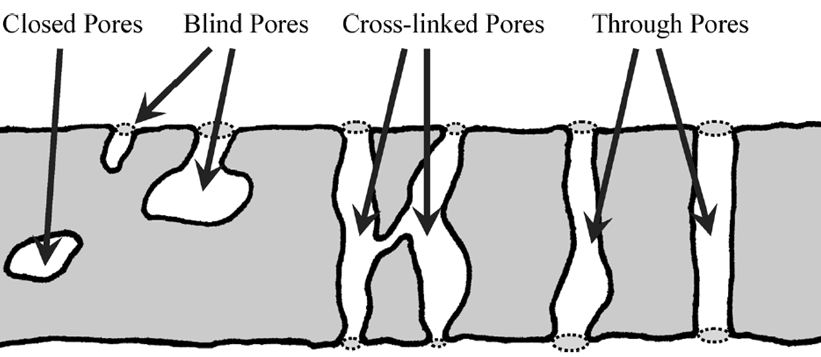 Pycnometry & Porosimetry
Pycnometry & Porosimetry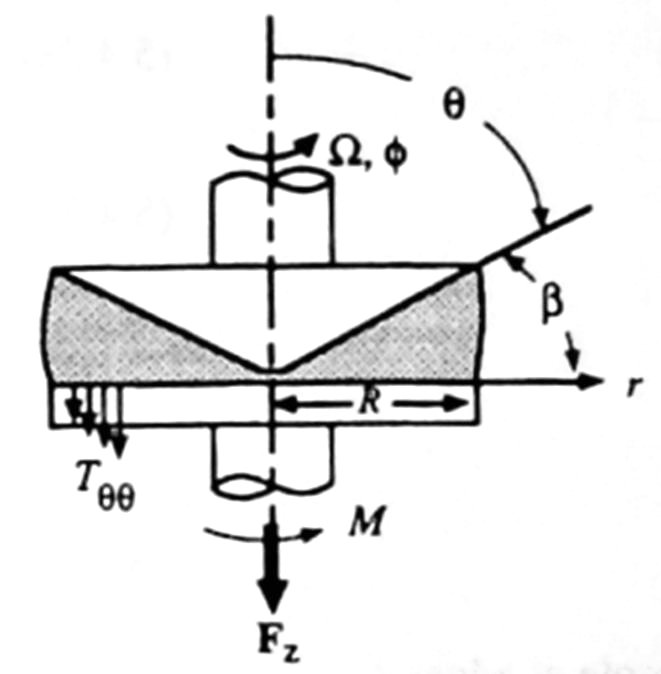 Rheometry
Rheometry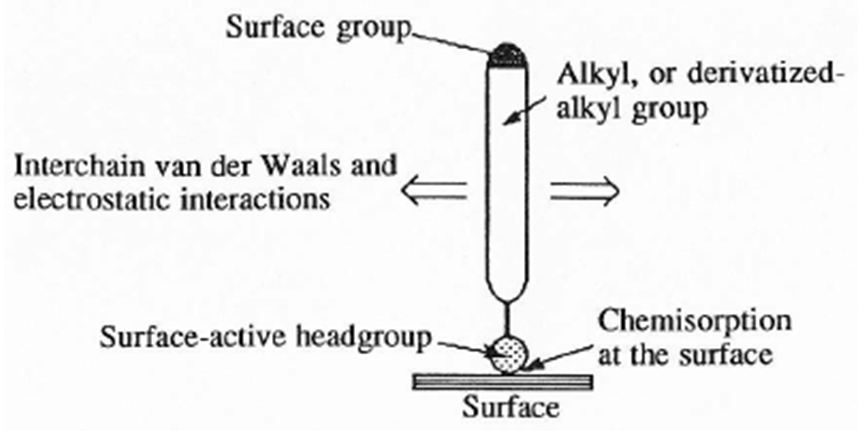 Self-Assembled Monolayers
Self-Assembled Monolayers Spectroscopic Ellipsometry
Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Spin Coating
Spin Coating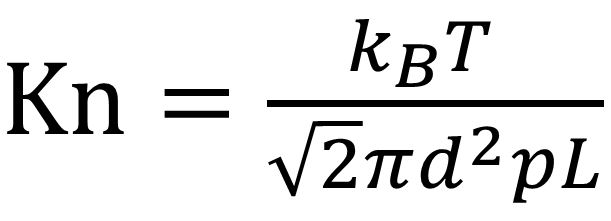 Thin Film Deposition
Thin Film Deposition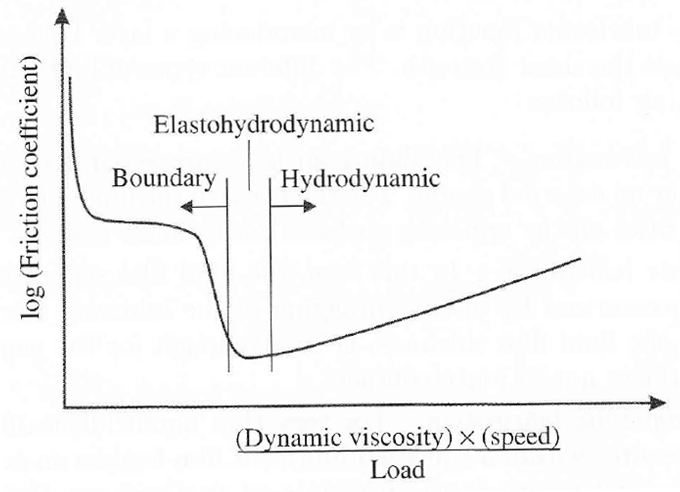 Tribological Analysis
Tribological Analysis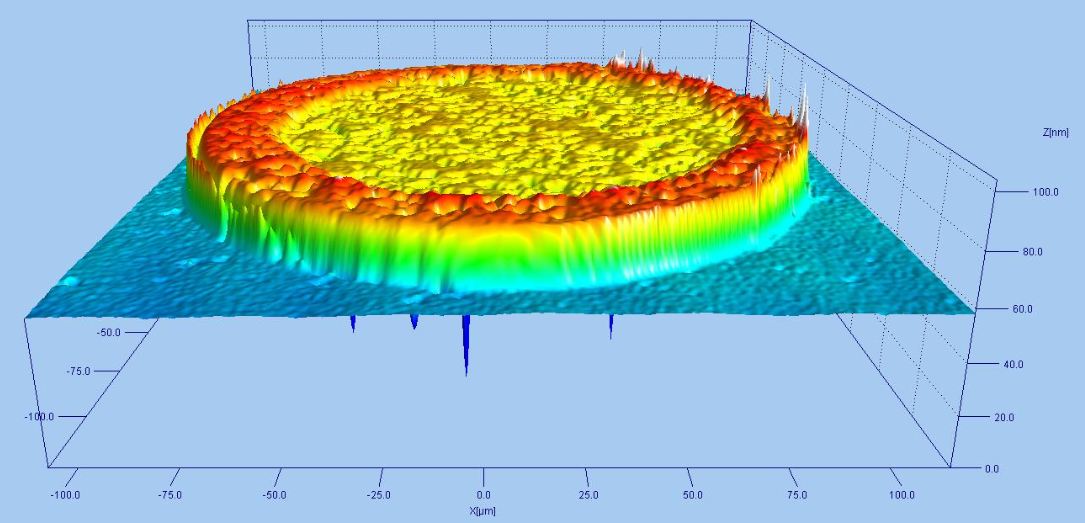 White Light Interferometry
White Light Interferometry.JPG) X-Ray Diffraction
X-Ray Diffraction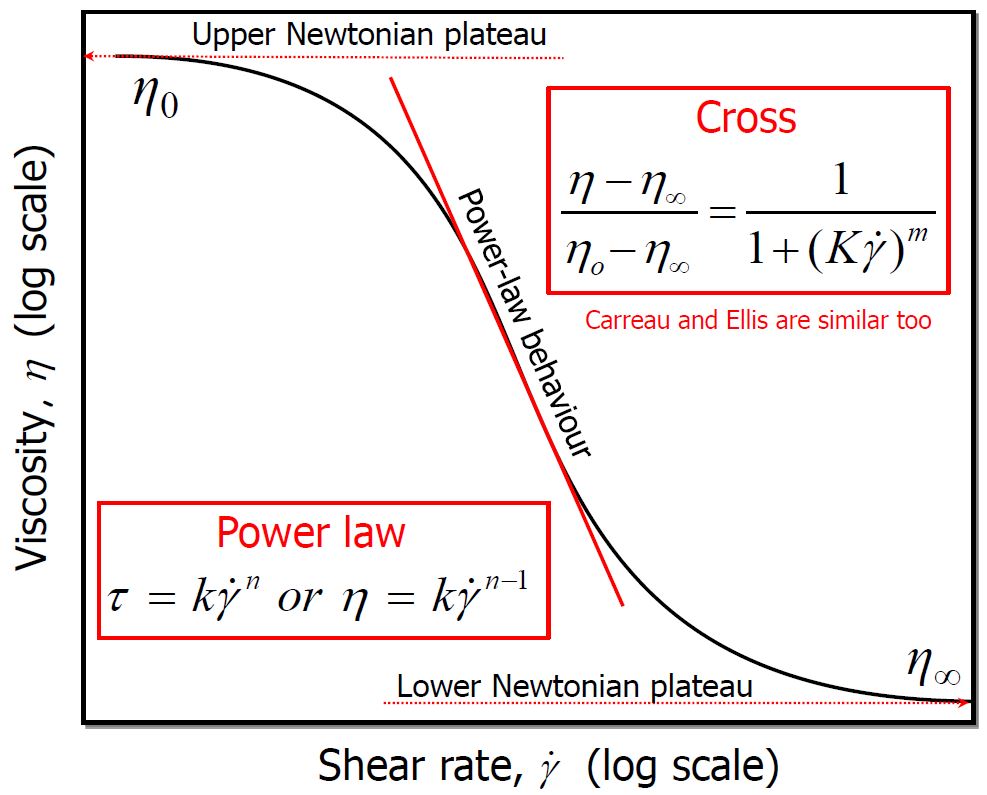 Colloids and Rheology
Colloids and Rheology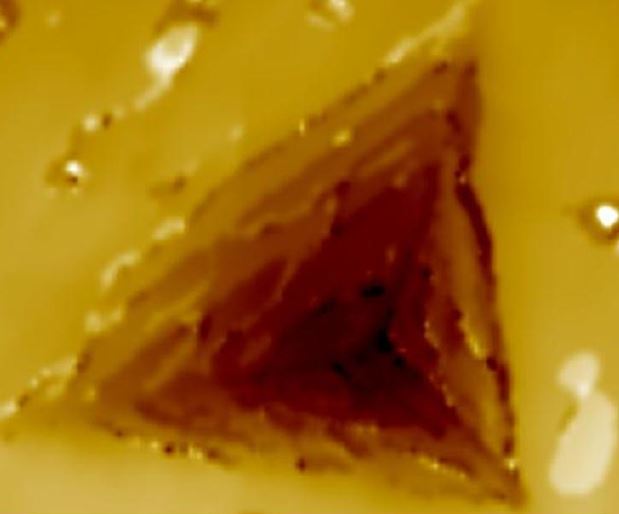 Measurement Techniques
Measurement Techniques Multiphase Systems (3MS)
Multiphase Systems (3MS) Nanoscale Engineering (T366)
Nanoscale Engineering (T366)